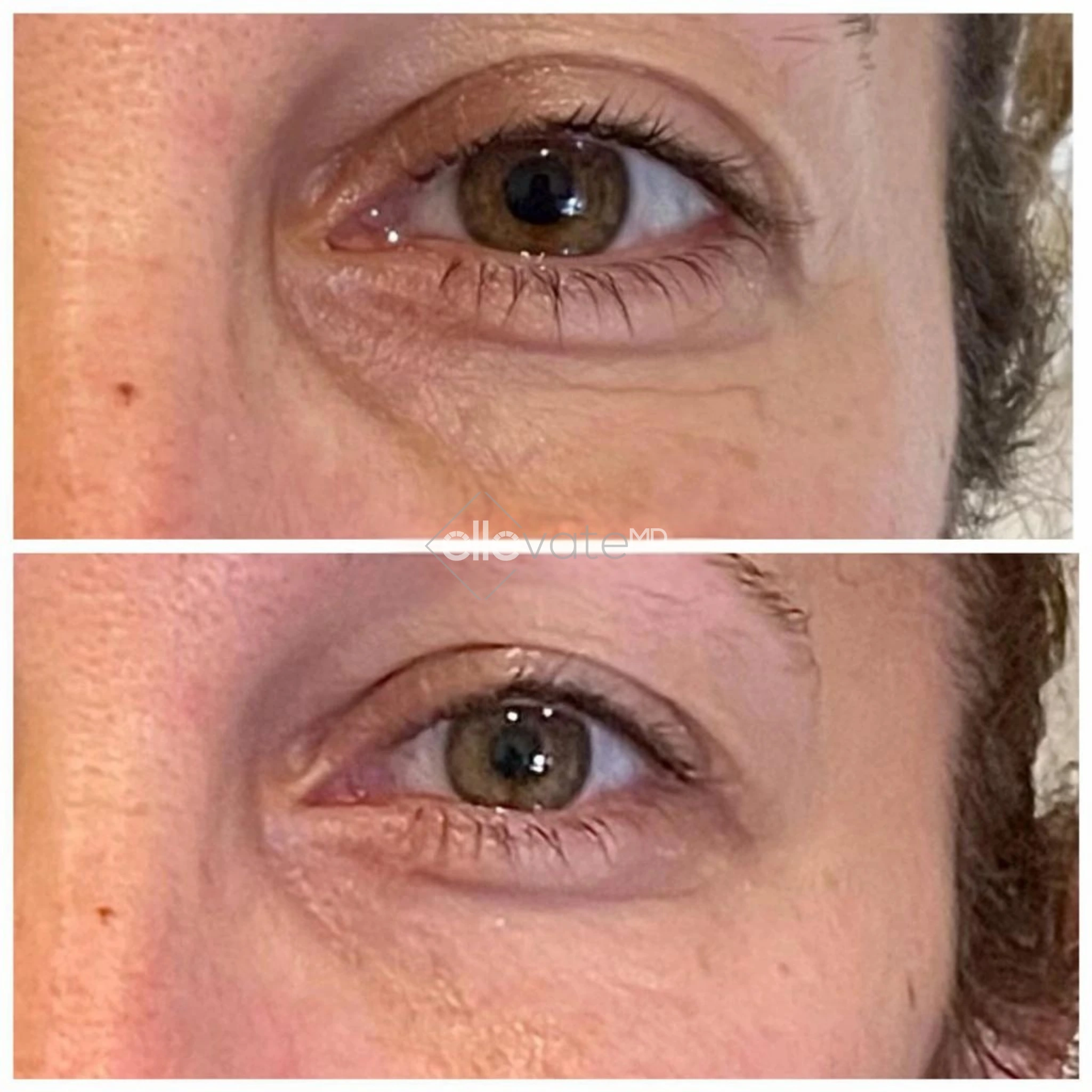
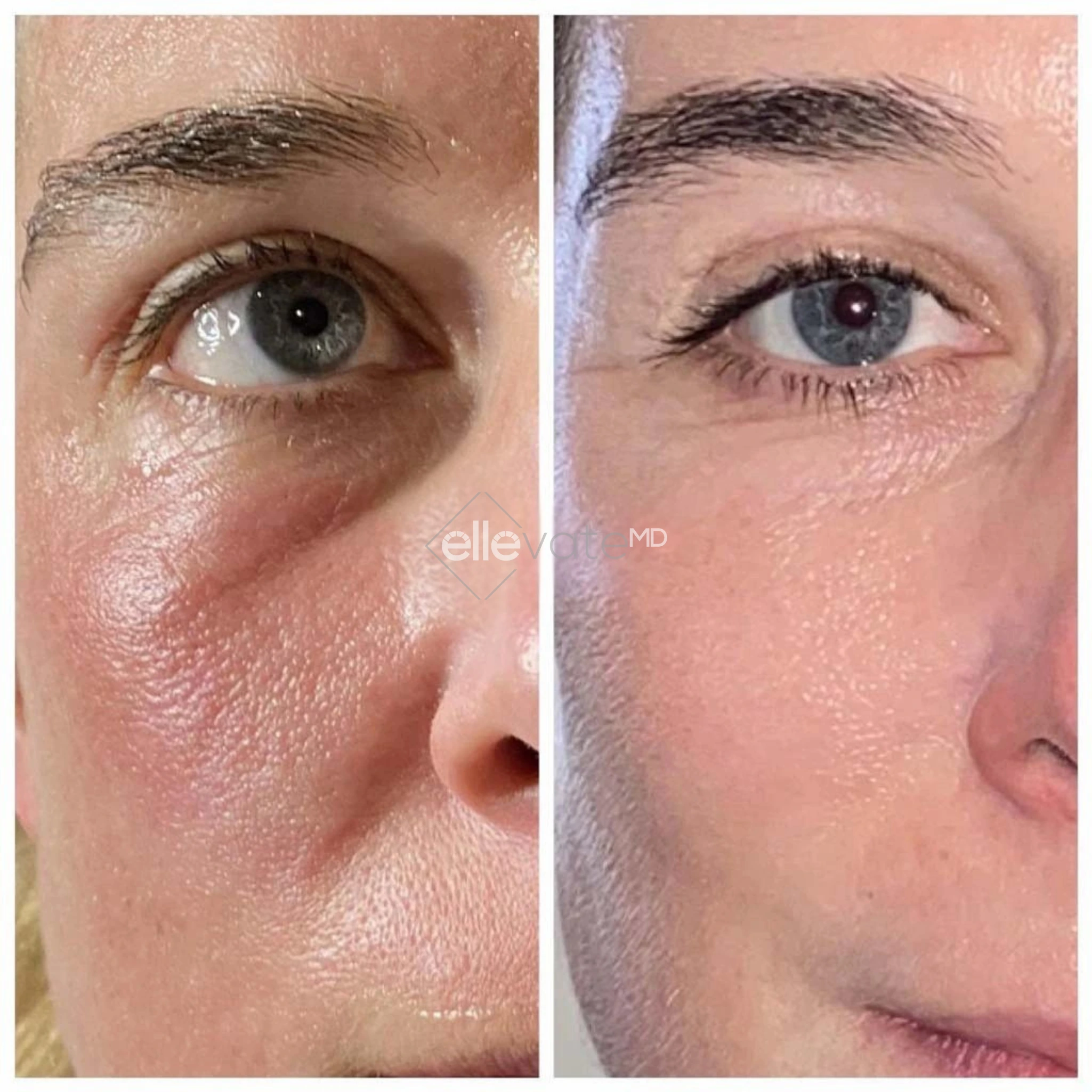
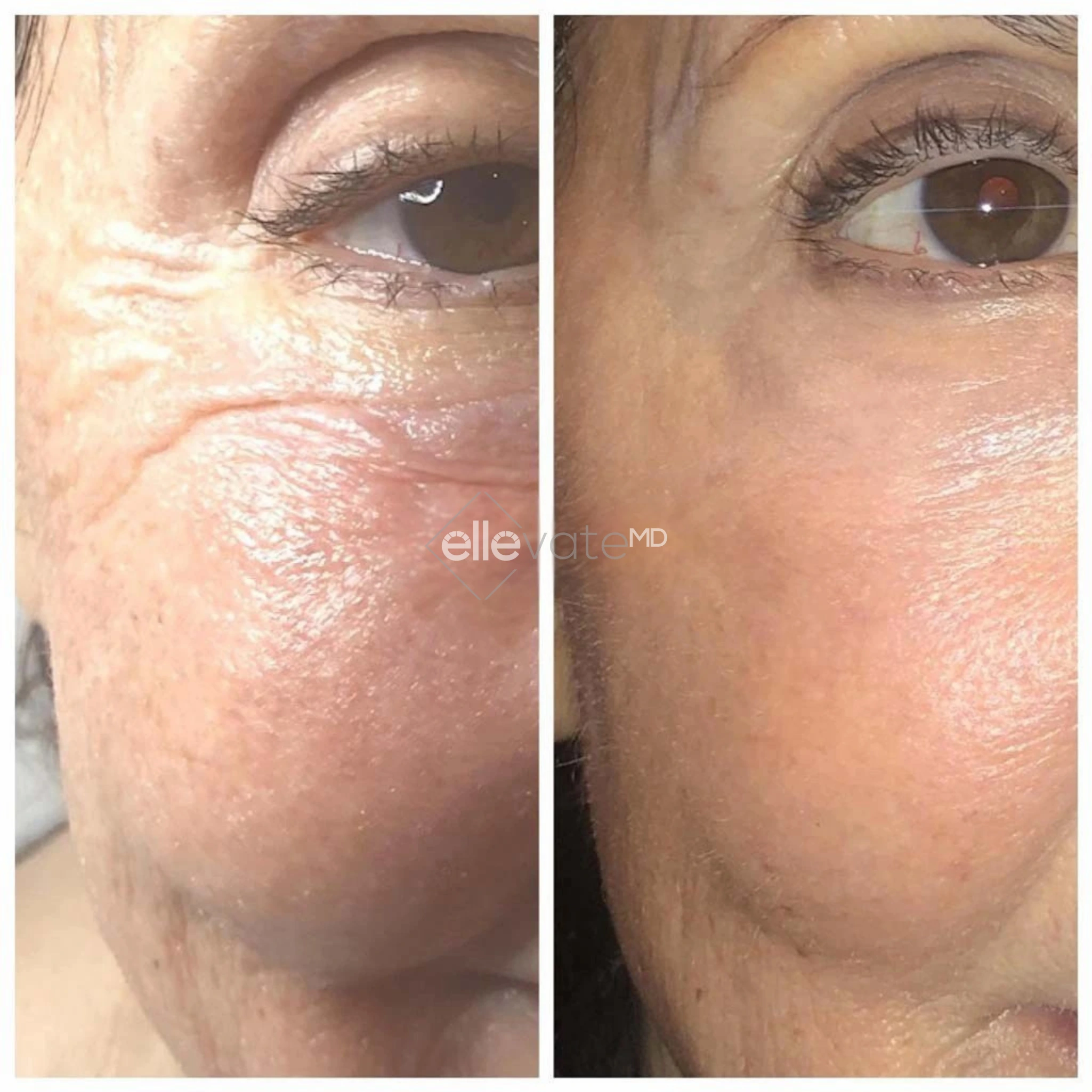
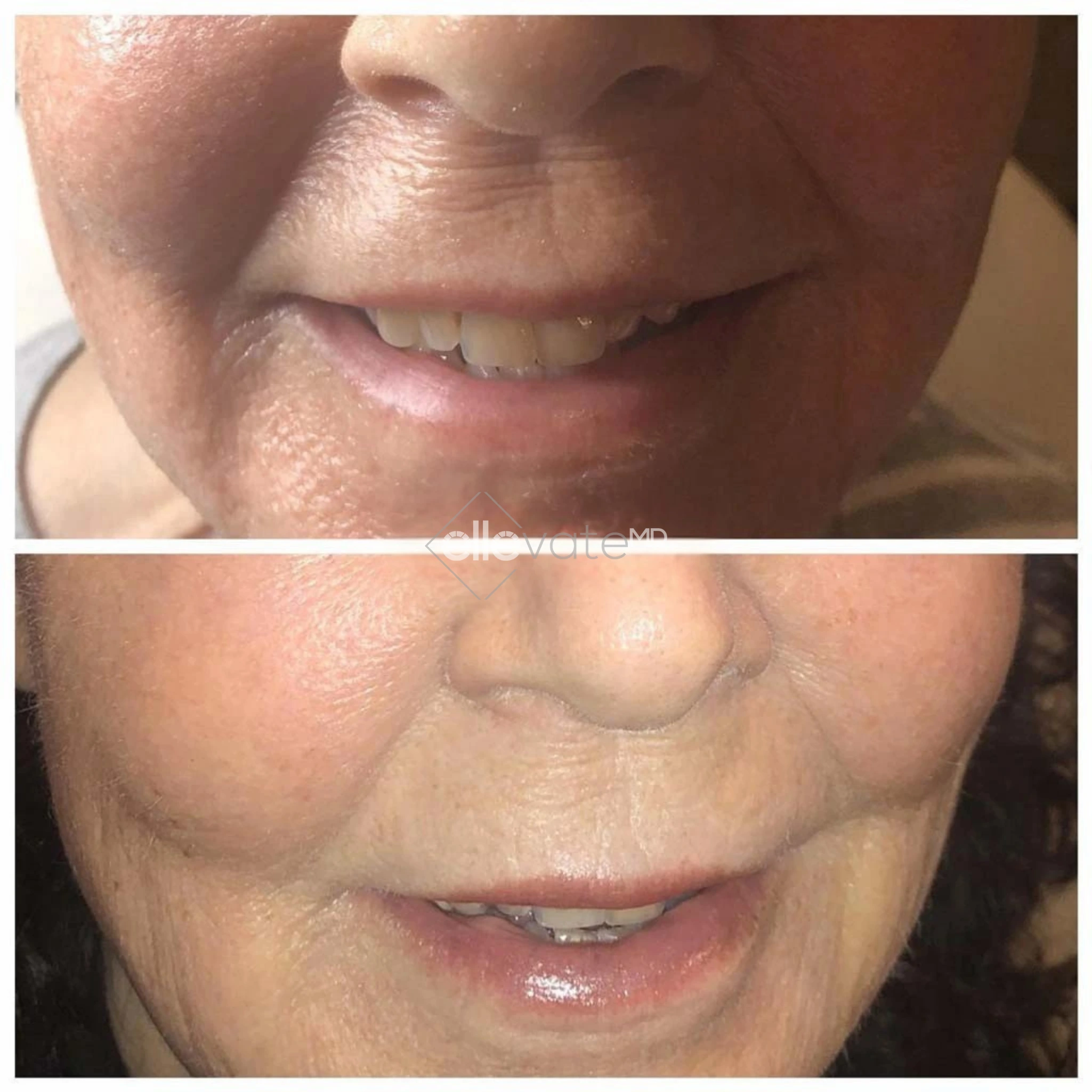
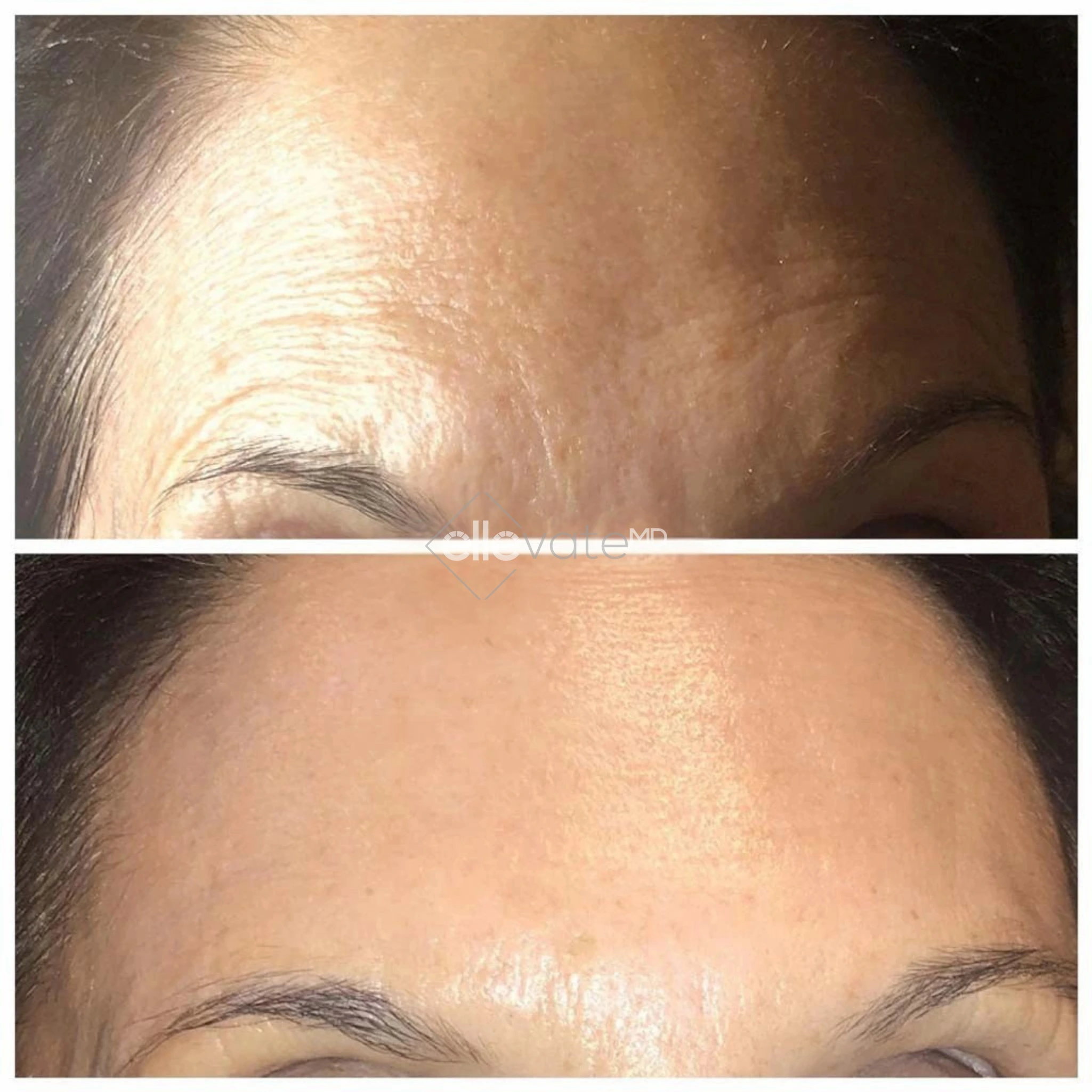
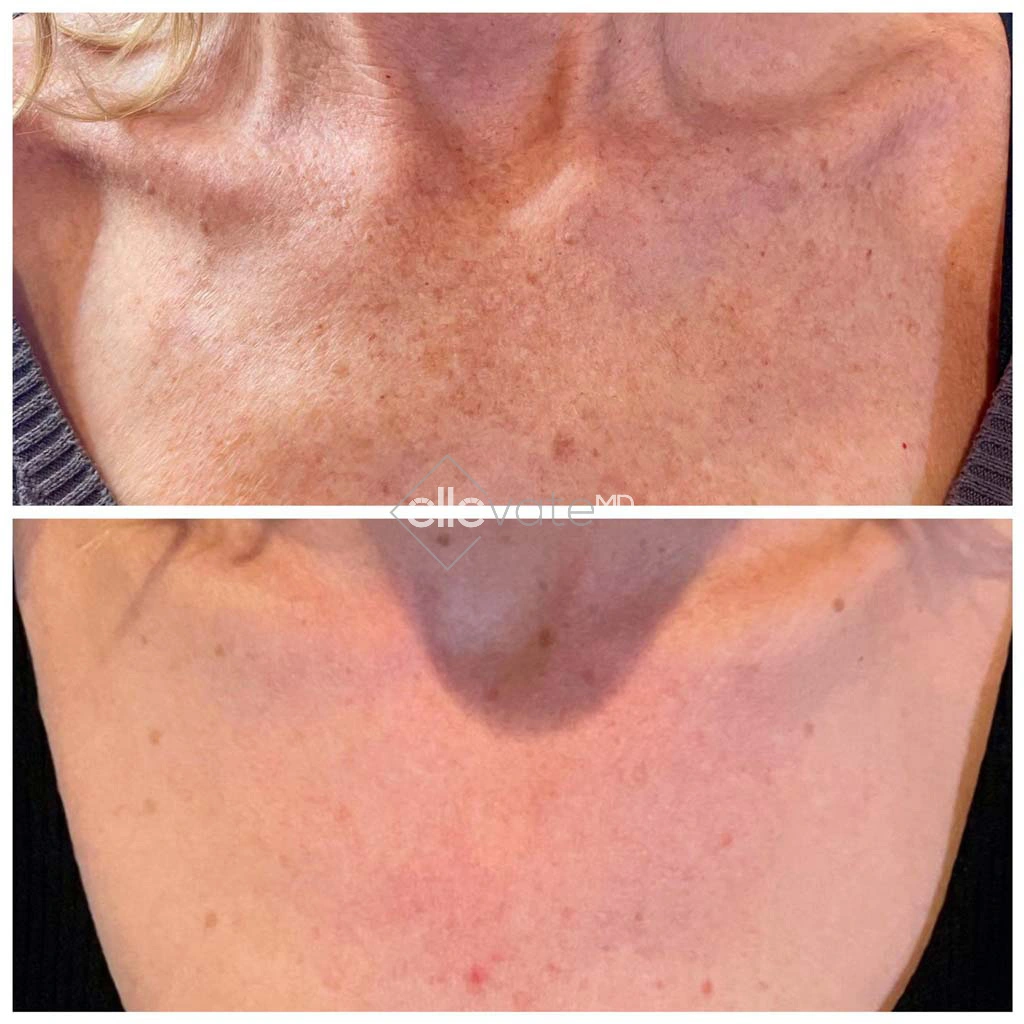
Tirzepatide vs. Diet & Exercise Alone: What Science Shows

Table of contents
1.
2.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
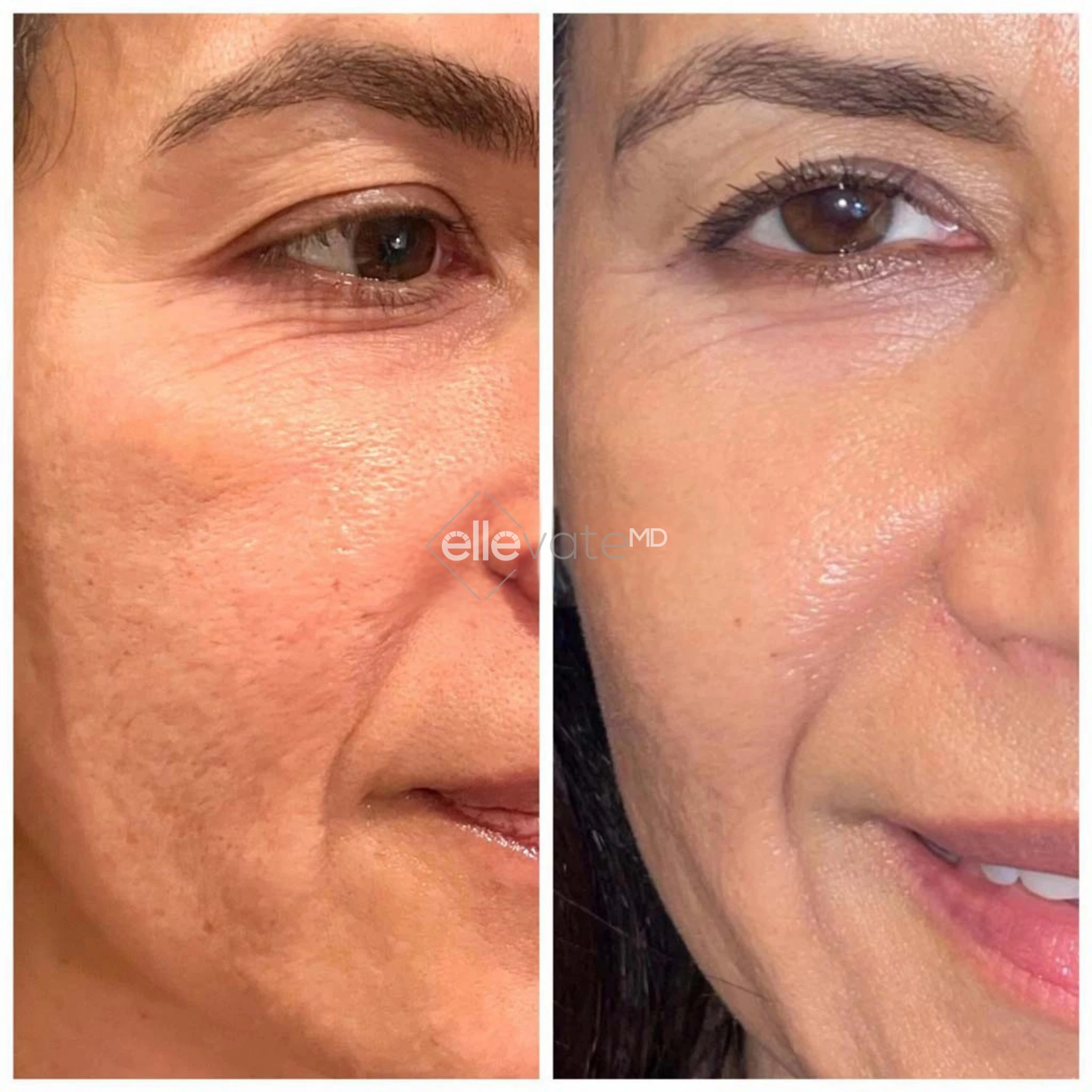
When it comes to weight loss, the debate between medication and lifestyle changes has intensified with the emergence of drugs like tirzepatide. The scientific evidence reveals that while diet and exercise remain foundational, tirzepatide produces significantly greater weight loss – typically 15-20% of body weight compared to 5-10% with lifestyle interventions alone. However, the most effective approach combines both strategies, addressing not just the number on the scale but overall metabolic health and sustainability.
Understanding Tirzepatide and How It Works
Tirzepatide represents a breakthrough in obesity treatment. This medication works by mimicking two natural hormones: GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). These hormones regulate appetite, slow stomach emptying, and improve how the body processes sugar and fat.
Unlike traditional diet pills or stimulants, tirzepatide addresses the biological mechanisms that make weight loss difficult to achieve and maintain. It essentially recalibrates the body’s set point for weight, making it easier to eat less without the constant feeling of deprivation that often accompanies conventional dieting.
Changes in Body Weight: Comparing the Numbers
The differences in weight loss outcomes between tirzepatide and lifestyle interventions alone are striking. Clinical trials show that adults with obesity taking the highest dose of tirzepatide (15 mg) lost an average of 20.9% of their body weight over 72 weeks. In contrast, the control group using diet and exercise alone lost approximately 3.1% of their body weight during the same period.
For overweight or obese patients, this translates to real-world differences. A person weighing 250 pounds might lose 50 pounds with tirzepatide plus lifestyle changes, compared to 12-15 pounds with lifestyle modifications alone. These aren’t just cosmetic improvements – they represent meaningful reductions in health risks.
Research consistently demonstrates that tirzepatide produces weight loss approximately 3-4 times greater than intensive lifestyle interventions when measured head-to-head. Even compared to the most rigorous diet and exercise programs, the medication yields superior results for the majority of participants.
How Do Intensive Lifestyle Interventions Lead to Weight Loss?
The mechanism centers on creating a caloric deficit through reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure. Structured programs typically involve nutrition counseling, meal planning, portion control, and regular physical activity – usually at least 150-300 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
The challenge with lifestyle modification lies in biological adaptations. When we lose weight through diet and exercise, our bodies respond by decreasing metabolic rate and increasing hunger hormones. This evolutionary survival mechanism makes it progressively harder to continue losing weight and easier to regain it. Studies show that only about 20% of people who lose significant weight through lifestyle changes alone maintain that loss long-term.
Intensive programs that include behavioral therapy, regular check-ins, and support groups show better outcomes than self-directed efforts. However, even the best programs struggle with the body’s powerful biological drive to defend its previous weight.
Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Beyond the Scale
Perhaps the most important consideration isn’t just weight loss but improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors. Both approaches offer benefits, but the magnitude differs significantly.
- Tirzepatide consistently demonstrates impressive improvements in markers like hemoglobin A1C (a measure of blood sugar control), with reductions of 2% or more in people with type 2 diabetes. It also improves cholesterol profiles, reduces liver fat, and decreases inflammation markers throughout the body. These changes reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other obesity-related complications.
- Diet and exercise alone also improve these markers, but typically to a lesser degree. A well-designed lifestyle program might reduce A1C by 0.5-1%, improve cholesterol modestly, and provide cardiovascular benefits through improved fitness. The key advantage of lifestyle interventions is that they provide benefits independent of weight loss – exercise strengthens the heart and improves insulin sensitivity even without significant weight reduction.
Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Health
Blood pressure improvements represent another critical comparison point.
- Tirzepatide trials show systolic blood pressure reductions of 7-10 mmHg on average, with some participants experiencing even greater drops. These reductions are clinically significant and can mean the difference between needing blood pressure medication and not.
- Lifestyle interventions, particularly those emphasizing the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet and regular aerobic exercise, can reduce blood pressure by 5-8 mmHg. While this is meaningful, the combination of medication and lifestyle changes produces the most dramatic improvements, sometimes allowing people to reduce or eliminate blood pressure medications entirely under medical supervision.
The cardiovascular benefits extend beyond blood pressure. Recent data suggests that GLP-1 receptor agonists (a related class of medications) reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events. While long-term cardiovascular outcome studies for tirzepatide are ongoing, early indicators are promising.
Quality of Life: The Human Experience
Quality-of-life improvements matter as much as clinical measurements. Adults with obesity often experience limitations in mobility, chronic pain, sleep apnea, depression, and social stigma. Both approaches address these issues, but through different timelines and mechanisms.
People taking tirzepatide often report rapid improvements in energy levels, mobility, and self-esteem as weight drops. However, the medication can cause side effects – primarily nausea, diarrhea, and constipation – that affect quality of life, especially during the first few weeks or after dose increases. These side effects typically diminish over time but can be significant enough that some people discontinue treatment.
Lifestyle interventions improve quality of life through multiple pathways. Regular exercise boosts mood through endorphin release, improves sleep quality, and builds physical capability. The sense of accomplishment from achieving fitness goals provides psychological benefits that medication alone cannot replicate. However, the process is slower and requires consistent effort that can feel overwhelming.
Clinical Practice: Integrating Both Approaches
In clinical practice, the most successful outcomes occur when tirzepatide and lifestyle interventions work together rather than as competing alternatives. Physicians increasingly prescribe tirzepatide as part of a comprehensive weight management program that includes nutritional counseling, exercise recommendations, and behavioral support.
This combination approach makes sense biologically. Tirzepatide handles the hormonal and appetite aspects that make weight loss difficult, while lifestyle changes address fitness, muscle preservation, nutritional adequacy, and long-term habit formation. Patients who maintain healthy eating patterns and regular exercise during medication treatment typically achieve better results and are more likely to maintain their weight loss if they eventually discontinue the medication.
Healthcare providers emphasize that tirzepatide isn’t a shortcut or “easy way out” – it’s a medical tool that addresses the biological aspects of obesity as a chronic disease. Just as we don’t tell people with high blood pressure to rely solely on lifestyle changes when medication is indicated, adults with obesity shouldn’t feel they must struggle with willpower alone when effective treatments exist.
Our Tirzepatide Program Offers Professional Care for Adults with Obesity
At ellevateMD, our tirzepatide program is designed for individuals who are ready to transform their health. Our comprehensive approach begins with a thorough evaluation of your medical history, body mass index, and cardiovascular risk factors to determine if tirzepatide is right for you.
We understand that obesity management requires more than just a prescription. Our team works closely with each patient to decrease baseline body weight safely and effectively while addressing your unique diet and exercise goals. We monitor treatment efficacy throughout your journey, tracking not just the numbers on the scale but the broader health benefits you experience – from improved energy levels to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Our program is also designed for individuals with severe obesity or those whose body mass index indicates significant health risks. We carefully screen patients to ensure safety, excluding those with conditions like unstable major depressive disorder or other contraindications. Our goal is to help you achieve optimal control over your weight and metabolic health through personalized medical supervision, nutritional guidance, and ongoing support.
Ready to explore whether tirzepatide could be part of your weight management solution? Contact ellevateMD today to schedule your consultation and take the first step toward lasting change.
Final Thoughts on Tirzepatide vs Lifestyle Modifications for Obese Patients
The evidence comparing tirzepatide vs lifestyle weight loss demonstrates compelling advantages for medication-assisted chronic weight management. Double-blind placebo-controlled studies consistently show that the body weight loss achieved with tirzepatide far exceeds what the placebo group accomplishes through lifestyle changes alone, with statistical analysis revealing an estimated treatment difference of 15-20 percentage points by week 72.
Beginning with the starting dose and progressing to the maximum tolerated dose, patients experience clinically meaningful weight loss that addresses weight-related comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus, obstructive sleep apnea, and other conditions. Tirzepatide, compared to lifestyle interventions, shows superior results in reducing baseline body weight and meeting weight-reduction thresholds. Treatment discontinuation rates remain relatively low despite the most common adverse events, such as nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
When examining lifestyle weight loss compared to medication approaches, the data reveals essential nuances about the treatment of obesity. Patients who maintain a diet and exercise log and work toward their goals can achieve initial weight loss and health benefits, particularly those without severe obesity. The percent weight change and secondary outcomes measured in clinical trials show that tirzepatide’s maximum tolerated dose produces greater improvements in improving cardiometabolic risk factors and decreasing cardiovascular mortality compared to lifestyle modification alone. The clinical characteristics of study participants help predict treatment efficacy, with those having higher baseline weight often experiencing more dramatic reductions in baseline body weight percentages, though some individuals with eating disorders and other severe psychiatric disorders require careful screening before treatment.
Ultimately, the path to sustainable health outcomes depends on individual circumstances, medical history, and goals. For some, lifestyle interventions provide sufficient weight management; for others, particularly those meeting criteria for bariatric surgery or with multiple weight-related conditions, tirzepatide offers transformative results that lifestyle changes alone cannot match. The ideal approach integrates both strategies – medication to address biological barriers while building the habits necessary for long-term success.